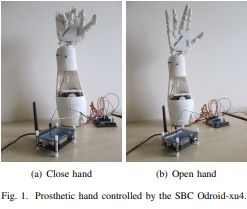
Embedded Brain Machine Interface based on motor imagery paradigm to control prosthetic hand
Resumen: Brain Machine Interfaces (BMI) have been developed as an alternative way to decode brain signals into control commands and communication devices. A typical BMI uses a computer to process EEG signals; however, current embedded PCs have enough computational resources for fully embedded BMI systems. In this work, the performance of the Odroid-xu4 embedded PC is evaluated as a processing and control device for BMI based on a 2-class motor imagery paradigm. Results show the best accuracy (82.1%) using SVM classifier and minimal processing times (0.11s) on the embedded device, which allows the development of a portable, low cost and trustworthy system.
Autor(es):ACUÑA, K.; CARRANZA, E.; ACHANCCARAY, D.
Año: 2016
Título de la revista: ANDESCON, 2016 IEEE
Ciudad: Arequipa, Peru
Página inicial - Página final: 1-4
Url: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7836266/