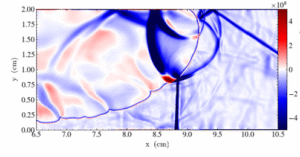
This study numerically investigates premixed flame propagation dynamics accounting for two different wall boundary conditions: (i) free-slip and (ii) non-slip boundary conditions. Direct numerical simulations (DNS) conducted here involved the solution of the fully compressible Navier–Stokes equations coupled with a 21-step chemical kinetic mechanism and full transport properties to quantify the influence of pressure waves on flame propagation. The analysis focuses on primary mechanisms driving flame propagation in confined. Accordingly, the effects of pressure waves on flame dynamics are analyzed, with particular attention to flame shape evolution. In particular, the Rayleigh-Taylor (RT) instability, closely linked to the thermoacoustic instability, and its effect on the flame corrugation are analyzed through the baroclinic torque. The results highlight hat under non-slip conditions, a distorted tulip flame (DTF) forms after the initial tulip flame, strongly influenced by reflected pressure waves and pressure gradients in the reacting flow. Additionally, using Spectral Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (SPOD), a strong coupling between reflected pressure waves, vortex formations, and shape evolution is observed. Particularly, harmonic structures are identified in the pressure wave reflected by the channel end wall that leads to higher harmonics around the flame front due to the non-linear interaction between pressure waves and flame front.
Autor(es):ILLACANCHI, Fernando
MENDIBURU, Andres
BRAVO, Luis
KHARE, Prashant
CELIS, Cesar
Año: 2025
Título de la revista: International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer
Volumen: 169
Número: 109810
Url: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2025.109810
