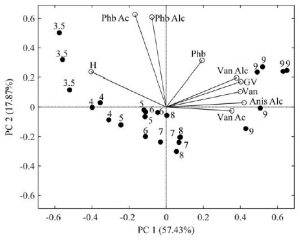
This study provides the first chemical investigation of wild-harvested fruits of Vanilla pompona ssp. grandiflora (Lindl.) Soto-Arenas developed in their natural habitat in the Peruvian Amazon. Flowers were hand-pollinated and the resulting fruits were analysed at different developmental stages using an HPLC-DAD method validated for the quantification of glucovanillin and seven other compounds. LC–ESI-MS studies corroborated the identities of four glucosides and seven aglycones, among them vanillin (5.7/100 g), 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol (3.6/100 g), and anisyl alcohol (7.1/100 g) were found in high concentrations. The attractive flavor/aroma profile exhibited by wild V. pompona fruits supports studies focused on the development of this species as a specialty crop.
Autor(es):19. Maruenda, H.; Vico, M.L.; Householder, E.J.; Janovec, J. P.; Cañari, C.; Naka, A.; Gonzalez, A.E.
Año: 2013
Título de la revista: Food Chem.
Volumen: 138
Número: 1
Página inicial - Página final: 161-167
Url: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814612015543
